Urinary Incontinence: Types, Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
Urinary Incontinence: Types, Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
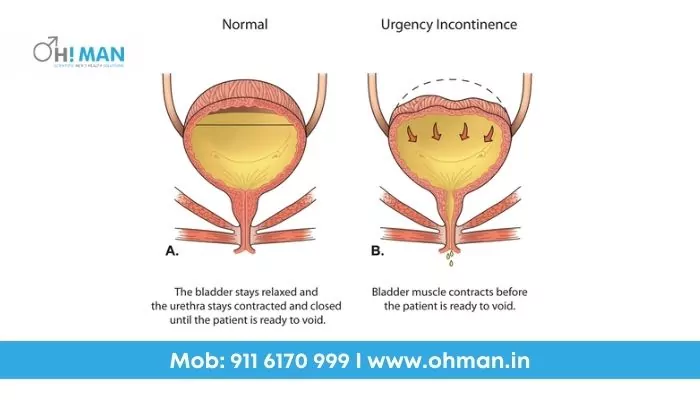
Urinary incontinence is refer as the loss of bladder control that causes uncontrol urination. It is commonly observed among older Men and Women who gave birth or experienced menopausal changes. Urinary tract infections (UTIs), pelvic floor issues, and an overly large prostate are also reasons.
Table of Content –
- Defining Urinary Incontinence
- Different Types Of Urinary Incontinence
- Who Is At A High Risk Of Suffering From Urinary Incontinence?
- Causes Of Urinary Incontinence
- Urinary Incontinence Symptoms
- Diagnosis Of Incontinence
- Treating Urinary Incontinence
- Lifestyle Changes For Urinary Incontinence
- Bottom Line
- Frequently Asked Questions
Defining Urinary Incontinence
Urinary incontinence in the urinary tract is a condition that can affect many people’s lives. If you suffer from incontinence, you might suffer from bladder control issues and leak urine, and this leakage can be difficult to control and negatively impact your daily life.
The urinary system comprises the kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra, and these organs do several jobs. They filter and store waste in your body, and your kidneys act as the filter in your system. Further, the waste products eliminate from your blood through the kidneys, which create urine. The urine then pumps through two tubes; the ureters and the ureters are connected to the bladder. The bladder roles as an empty storage tank. As a result, the urine will stay in the bladder till the time comes for it to exit the body. When the bladder fills, the brain indicates that it’s time for you to urinate.
Urine goes out of the bladder once the muscle relaxes (sphincter), allowing the urine to flow out of the body via the urinary tract.
When the system is functioning well, you will typically have enough time to go to the bathroom before urinating. You don’t notice the leakage or leakage. However, urinary incontinence can signify that these organs don’t function as they ought to. It could be due to various reasons all through your life.
Many believe that urinary incontinence is inevitable in aging and has no possible treatment. While it’s true that the risk of incontinence is higher with age, there are other ways to deal with this issue. Incontinence doesn’t need to interrupt your daily life or prevent you from enjoying your life.
Different Types Of Urinary Incontinence
Urinary incontinence exists in a range of forms.
Each has its causes, characteristics, and triggers for urinary leakage. It is imperative to identify the type of incontinence to implement the treatment plan properly.
These are the types of incontinence:
Urge Incontinence
Urge incontinence occurs when you have an urgent need to empty your bladder. So, this can happen too fast for you to go to the toilet and have a lot of urine. A condition known as an overactive bladder can cause urinary incontinence. OAB can be caused by several factors, including weak pelvic muscles, nerve damage, or an infection. OAB can also be caused by certain medications and certain beverages, like alcohol or caffeine.
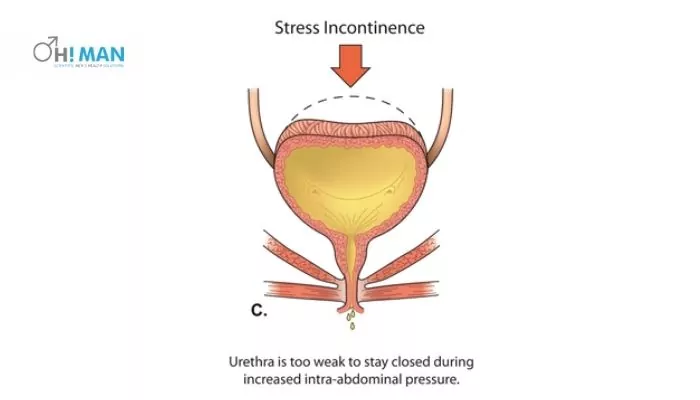
Stress Incontinence
This urinary incontinence occurs when you leak urine during an activity. This type of incontinence occurs when your pelvic floor muscles become weaker and don’t support your pelvic organs properly. You are more likely to leak urine from your body because of this weakness accidentally.
Many people experience leakage problems when they laugh, cough or sneeze. These actions put pressure on the bladder, and you are more likely to leak urine if you don’t have strong pelvic muscles.
Further, stress incontinence is more common in women who have had children. Stress incontinence may also occur in men who have undergone any kind of prostate surgery like prostate cancer surgery.
Overflowing Incontinence
If your bladder isn’t emptying every time you urinate, you might have overflow incontinence. Overflowing incontinence patients don’t empty their bladder, which puts them at risk of spillage. Further, this causes small amounts of urine to leak out over time, rather than one large gush.
Additionally, people with chronic conditions such as multiple sclerosis (MS), diabetes, or stroke are more likely to experience incontinence, and men with a large prostate may also experience this.
Mixed Incontinence
A combination of several issues that all lead to leakage can cause mixed incontinence. Stress incontinence or an overactive bladder can cause mixed incontinence. Knowing what you are doing is important when you experience leakage problems with mixed incontinence.
Further, finding what triggers mixed incontinence is often the best way to manage mixed incontinence.
Functional incontinence
In the situation of functional incontinence, although the urinary function of the bladder is normally functioning, the patient isn’t able to go to the bathroom on time. Physical impairment could cause it, such as arthritis or mental illness like Alzheimer’s disease.
Incontinence overflow
A small amount of urine dribbles when a patient suffers from significant residual post-void urine—further, enlarged prostate or spinal injury leads to insufficient bladder drainage.
Who Is At A High Risk Of Suffering From Urinary Incontinence?
You are at greater risk for developing urinary incontinence if you take the following steps:
- Gender. Women are more probable to experience stress incontinence. So, This is due to pregnancy, childbirth, menopause, normal female anatomy, and pregnancies. Overflow and urge incontinence are more prevalent in men with prostate issues.
- Age. With age, your bladder muscles and urethra muscle strength decreases. The quantity of urine your bladder can retain decreases as you get older, which increases the chances of involuntary urinary flow.
- Overweight. More weight can cause pressure on your bladder, surrounding muscles, and kidneys. So this causes urine to leak when you cough or sneeze.
- Do not smoke. Tobacco smoking may increase your risk for urinary incontinence.
- Family history. Urinary incontinence is more common in close relatives, particularly urge incontinence.
- Certain diseases. Diabetes or neurological conditions may increase the risk of incontinence.
Causes Of Urinary Incontinence
Both the causes and the type are closely connected.
Stress incontinence
Factors include:
- Pregnancy and childbirth
- Menopause, falling estrogen can cause weaker muscles.
- Hysterectomy and other surgical procedures
- Age
- obesity
Urge incontinence
These are the causes of urge incontinence.
- Cystitis is an inflammation of the bladder’s lining.
- neurological conditions, like stroke, multiple sclerosis (MS), and Parkinson’s disease.
- An enlarged prostate can lead to a drop in the bladder and irritated urethra.
Overflow Incontinence
This is triggered by a bladder obstruction or blockage. An obstruction could be caused by the following:
- An enlarged prostate gland and Infection like prostatitis
- Constipation
- The incontinence surgery for urinary incontinence went too far.
Total incontinence
It could be:
- An anatomical defect that is present since birth
- A spinal cord injury that impairs nerve signals between the brain and bladder
- A fistula is a tube-like channel that develops between the bladder, and another area, usually the vaginal area.
Other causes
These include:
- Some medications, including diuretics and antihypertensive drugs and sleeping tablets, sedatives, and muscle relaxants, may be affected by certain medications.
- alcohol
- Urinary tract infections
Urinary Incontinence Symptoms
It is important to note that urinary incontinence is a symptom of more serious medical conditions that can damage the urinary tract muscles and functional or incontinence. The symptoms that can accompany urinary incontinence include:
- More frequent urination, especially at night (nocturia)
- Bedwetting
- Urinary urge increases leading to spasms in the pelvic region

Diagnosis Of Incontinence
These are the techniques used to diagnose urinary incontinence.
- A physical examination: The doctor examines the patient to determine if there are any abnormalities, such as a weak pelvic floor muscle in women or enlarged prostate in men.
- Urinalysis is a test to identify urinary tract infections, blood in the urine, and some other irregularities in the urine.
- The postvoid residual (PVR) is a test that determines how much urine remains after urinating.
- Urodynamic Testing: This test assesses the bladder and sphincter muscles’ ability to endure stress.
- Stress test: The stress test involves the patient applying sudden pressure to the doctor, who then evaluates for any leakage.
- Urodynamic testing evaluates the bladder and urinary tract muscle’s stress withstanding capacity.
- An X-ray process is used to produce a cystogram, which is a picture of the bladder.
- Cystoscopy is a procedure that involves introducing a thin tube with lens into the urethra. Any irregularities in your urinary system is visible to the doctor.
Treating Urinary Incontinence
There are many options available for urinary incontinence treatments:
- Medications: Many medications can help to treat the symptoms of urinary leakage. These medications are used to control overactive bladders and urge incontinence. Incontinence management is also possible by using nerve stimulators or bulking material injections.
- Exercises – Pelvic floor exercises, strengthen the power of bladder and sphincter muscles and minimize stress incontinence.
- Devices – Urinary Insert and Pessary may be helpful for women with urinary incontinence.
- Surgery: The following surgical interventions can be used to treat urinary incontinence
- Slinging procedures
- Bladder neck suspension
- Prolapse surgery
- Artificial urinary sphincter
- Behavior techniques: Fluid management, training for emptying the bladder, and double voiding, can all help manage urinary incontinence.
Lifestyle Changes For Urinary Incontinence
You can make some changes to your daily life that could help with your incontinence. Further, these changes are possible at home, so you don’t have to seek additional treatment.
So, the lifestyle changes to improve urinary incontinence include:
- Regularly empty your bladder.
- Before you begin any physical activity, empty your bladder.
- Avoid lifting heavy objects.
- Regular Kegel exercises can help strengthen your pelvic floor muscles.
- Before you start an activity, avoid drinking caffeine or too much fluids.
- A healthy weight is important.
- To help reduce the time it takes to go to the toilet, you can practice bladder training.
- Incontinence management can be made easier by using pads or products that catch urine.
Bottom Line
Inability to retain urine can lead to discomfort, embarrassment, and other problems. People can withdraw from their friends and family due to embarrassment, leading to depression. Consult your doctor immediately if you are concerned about your urinary incontinence.
At Ohman, our specialists can help men address their sexual health concerns. So, in case you are experiencing erectile dysfunction, premature ejaculation, or looking for general sexual wellness consultation, book an online consultation with Ohman.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is it possible to prevent urinary incontinence?
Ans – Although bladder control issues such as urine incontinence (UI) cannot always be avoided, healthy practices may help maintain your bladder healthy. Ensure a good body mass index (BMI). Further, do pelvic exercises. Caffeine, liquor, and acidic meals are all bladder irritants, so avoid them. Consume more fiber to avoid constipation, a common cause of urine incontinence.
Is urinary incontinence going to last for life?
Ans – Incontinence might be a temporary problem that goes away after addressing the underlying reason. This is often the case when you have a problem like a UTI, and a UTI’s frequent urine and leaking issues usually go away after it’s treated. However, if you have been diagnosed with any form of urinary incontinence, good therapy may be able to completely reverse it or, at the very least lower the symptoms.
How do you fix urinary incontinence?
Ans – Your doctor may prescribe you medication to treat urinary incontinence, and devices may suggest certain exercises or even surgery.
How to Perform Kegel Exercises?
Ans – The pelvic floor muscles, which control the bladder and intestines and impact sexual performance, maybe strengthened using kegel exercises for men.
Here is how to perform Kegels:
- Ensure your bladder is empty before sitting or lying down.
- Tighten the muscles in your pelvic floor. Hold your breath for 3 to 5 seconds.
- Count 3 to 5 seconds while relaxing the muscles.
- Perform Kegels 10 times and 3 times a day.



