Testicular Pain: Possible Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Testicular Pain: Possible Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments

“Testicular pain can be caused by several possible reasons ranging from traumatic injuries, nerve damage, Infections like sexually transmitted infections (STIs), kidney stones, inflammation, hernia, enlarged veins, or severe medical conditions like Testicular Cancer or testicular torsion.”
Testicular discomfort may occur at any age in males. It happens in the scrotum, a small pouch of skin that houses the testicles (testes) and tiny reproductive organs like an egg.
A person suffering from testicular pain can feel pain in one or both testicles. In addition, this pain may arise from within the testicle or other parts of the body, like the stomach or groin, which is known as referred pain.
There are two types of testicular pain: one is acute (sudden and brief), and the second is chronic (gradual and long-lasting).
→Acute scrotum discomfort is “the constellation of new-onset pain, swelling, and tenderness of the intrascrotal contents.”
→The term “chronic orchialgia” refers to testicular discomfort that lasts longer than three months and is highly uncomfortable to the patient.
Apart from these types of pain, symptoms of these pain may appear dull at first and increase with time & physical activity. You should get proper medical care if your testis pain lasts longer than an hour and become intense due to many sensitive nerves.
Table of Contents
Causes and Symptoms of Testicular Pain
Causes of Testicular pain caused by underlying diseases are as follows:

Testicular pain can be a cause of various underlying diseases. So if you are also going through pain, check out the following types of testicular pain and their symptoms, which might be causing pain in you too.
1. Testicular torsion
Testicular torsion is a rare but severe medical problem and testicular pain in men that happens when tissues are not attached well to the testicles. As a result, the testes may twist around the spermatic cord and cut off the blood flow to the testicle. It may happen during exercise, sitting, standing or even sleeping, generally occurring in 1 out of 4000 males below 25 or in teenagers causing severe pain. However, it causes pain and swelling more over the left testicle than the right testicle. In the case of Testicular torsion, immediate medical attention is required to solve this problem. Surgery is often used to unwind the testicles when the patient’s testicle can be saved. In Some cases where the blood supply to the testicle is wholly cut off, the doctor may remove that testicle with surgery.
Symptoms of Testicular torsion
Some of the symptoms you might face if you go through testicular torsion are as follows-
- nausea and vomiting.
- Swelling around the scrotum, sudden and severe pain in the scrotum or redness and darkening.
2. Varicoceles
Varicoceles, or “VAIR-ick-oh-seals,” an enlargement of the veins which reduces the blood flow and oxygen supply in the scrotum, the sac that houses and covers the testicles; it creates feeble pain in the testicles which affects 1 out of 5 men, which may increase with time and physical activities. Although, there is still not a clear picture of what causes Varicoceles & This problem is generally treated using a surgical process called Varicocelectomy.
Symptoms of Varicoceles
- Pain
- A mass in the scrotum
- Differently sized testicles
- Infertility
3. Orchitis
Orchitis is Bacterial or viral infection of the testicle, which causes painful inflammation of one or both testicles. The most common cause of viral orchitis is mumps(viral childhood disease)Bacterial. Orchitis is sometimes associated with untreated epididymitis, which can lead to Orchitis. Medical surgery for orchitis is required when pain can be unbearable and as severe as testicular torsion in males.
Symptoms of Orchitis
The common symptoms that you may experience if you go through the problem of Orchitis are as follows-
- fever, fatigue, or nausea.
- testicular pain
- Swelling in one or both testicles.
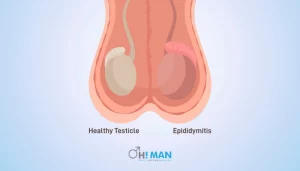
4. Epididymitis
Epididymitis is an inflammation of the sperm-carrying tube in the rear of your testicles called the epididymis. Bacteria E. coli causes epididymitis, Chlamydia or Mycoplasma transmitted through Urinary Tract Infections and Sexually Transmitted Diseases. This infection causes testicular pain and trouble in the testicles, which happens most often in people between the ages of 14 and 35. Generally, this problem is treated with antibiotics medicines.
Symptoms of Epididymitis
Some of the symptoms which you may go through if you suffer from Epididymitis infection are as follows-
- Swelling in the pubic region.
- Pin in the pubic area, which gradually increases with time.
- Scrotum feels hot to the touch.
Similarly, this problem can be caused due to urinary infections or can also result from sexually transmitted diseases such as gonorrhea. Doctors usually treat this problem in men with the help of antibiotics.
5. Testicular Cancer
Testicular cancer or testicular carcinoma is unusual compared to other cancers, which also cause testicular pain and are found in the scrotum, a loose pouch of skin under the penis; it develops when cells multiply faster than usual, eventually forming a lump or tumour and usually causes in 15 to 35 age male. Treatment of testicular cancer depends on several factors, including your health, treatment preferences, cancer stage, and tumour type.
Symptoms of Testicular Cancer
Testicular cancer symptoms and signs include:
- A growth or bump in either testicle
- A sensation of weight in the scrotum
- A dull ache in the abdomen or groin
- A sudden collection of fluid in the scrotum
- Testicle or scrotum pain or discomfort
- Enlargement or tenderness of the breasts
- Back pain
6. Testicular Lump
Most testicular lumps and swellings are caused by benign (non-cancerous) conditions, although occasionally, they can be a symptom of testicular cancer. However, the other symptoms of this problem are hernias and epididymitis. It is caused by something harmless, such as a fluid (cyst) build-up or swollen veins in the testicles (varicocele). If the lump or swelling is painful or very big, it is suggested to book an appointment with a specialist for an operation to drain, shrink or remove it.
Symptoms of Testicular Lump
Some of the other symptoms which you may face if you are going through the problem of a Testicular lump are as follows-
- Excessive swelling in the testicle.
- Feeling of a bump in the testicle area.
- A dull ache in the region of the groin.
7. Hernias
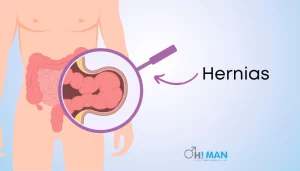
A hernia is a problem caused by tissue pushing through the abdominal muscles. An Inguinal Hernia can pass through the scrotum, inflaming the area around the testicles and producing discomfort and swelling. Inguinal and femoral hernias are due to weakened muscles that may have been present since birth or are associated with aging and repeated strains on the abdominal and groin areas.
However, the treatment process is ineffective for some reason, and Surgery can correct the placement of Hernias. The condition becomes worse when it happens with hydrocele, and treatment becomes complicated.
Symptoms of Hernias
- Swelling or bulge in the groin or scrotum (the pouch that contains the testicles).
- Increased pain at the site of the bubble.
- Pain while lifting.
- Increase in the bulge size over time.
- A dull aching sensation.
- A sense of feeling full or signs of bowel obstruction.
8. Kidney Stones
Kidney stones can cause pain that radiates to the testicles, and larger kidney stones may produce pain such as abdominal, groin pain, or Testicular pain Which the doctor called referred pain. For treatment, doctors generally opt for a surgical process to remove the stone from the kidney.
Symptoms of Kidney Stones
Some of the symptoms which you may go through if you have a kidney stone are as follows-
- feeling nauseous and urinating frequently.
- Blood in the urine or feeling a burning sensation during urinating.
- Pain at the upper side of the penis.
- Sharp and cramping pain groin.
When to see a doctor?
If you experience testicular discomfort or swelling, you should call your doctor immediately if the pain worsens or you feel unwell. Make sure to seek quick medical assistance if you have any testicular torsion symptoms.
Who treats testicular pain?
You should seek medical attention if you are experiencing testicular pain or if you recently engaged in high-risk sexual activity. Having several partners or a partner who has had multiple partners is high-risk sexual behaviour. The following specialists can diagnose you:
Urologist: An urologist may be seen if you exhibit symptoms of testicular cancer or kidney stones (a surgical specialist who treats urinary problems).
Andrologist – An andrologist who is specialized in providing proper and timely treatment for all male-factor infertility-related issues(testicular pain, sexual dysfunction) would be a better option.
Treatments for Testicular Pain
There are several treatments for testicular pain depending upon causes and symptoms. Some causes of testicular pain, like epididymitis, require medical treatment like antibiotics or anti-infective medicines. Other causes, like Testicular torsion and Orchitis, are chronic problems that require surgery.
Home Remedies for Testicular Pain

Your testicular discomfort could be manageable at home. Some cures to try are:
- Apply ice to the area.
- Some Exercises for testicle pain relief are Butterfly Stretch, Happy Baby, Frog Stretch and Piriformis Stretch.
- If you’re lying down, place a towel wrapped up beneath your scrotum.
- Wear a cup or athletic supporter.
- Take warm baths.
- Try non-prescription pain relievers.
Medical Treatment for Testicular Pain in Male
- Acetaminophen (Tylenol®) and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs), such as aspirin, ibuprofen, and naproxen, can help relieve pain. They are frequently recommended in situations of damage, trauma, or Orchitis.
- Antibiotics or anti-infective drugs: Antibiotics should be administered to treat bacterial infections that cause Orchitis or epididymitis.
- Tricyclic antidepressants: Nerve discomfort can be treated with drugs like amitriptyline.
Is Surgery needed for Testicular Pain?
Although testicular discomfort seldom requires Surgery, you could need it if you have an urgent condition like testicular torsion or testicular cancer.
Depending on the cause, many testicular surgery types include:
- Testicular de-torsion: This procedure aims to untwist the spermatic cord and allow blood to flow to the testicle (s). To stop the twisting from happening again, your surgeon sews sutures around your testicle. To avert future torsion, the opposing side of the testicle is also sewn.
- Hernia repair surgery is performed if your hernia cannot be forced back into your abdomen or made smaller.
- Epididymectomy: The epididymis is a network of skinny tubes that are tightly coiled and transport sperm from the testicles to the sperm ducts. If you experience persistent pain, a surgeon could remove your epididymis. It is uncommon to do this; instead, medical interventions are usually explored first.
- Vasovasostomy: Men who experience testicular discomfort after having a vasectomy can reverse the procedure with a vasovasostomy. Reversing the vasectomy can alleviate testicle pain brought on by vasectomies. Infrequently necessary, this is performed as an outpatient procedure.
- Shockwave lithotripsy: Shockwaves, or airborne force, are used to disintegrate kidney stones in this minimally invasive method.
- Microdenervation of the spermatic cord (MDSC): Under anaesthesia, this procedure is done. Testicular discomfort is frequently treated or alleviated by the surgeon using an operating microscope to dissect and sever the nerves going through the spermatic cord.
- Orchiectomy: Rarely, you may need to have the testicle removed if medicines or less invasive procedures do not relieve your testicular discomfort (orchiectomy). This is a last-ditch surgery.
- Testicular cancer: Your doctor performs Surgery to remove your testicles in this instance. The testicle is inspected under a microscope after the operation to determine the kind of testicular cancer. This decides if you require more therapy.
Remember that caring for your wound after Surgery is crucial to avoid infection regularly. Pay attention to your doctor’s instructions for cleaning your wound. Additionally, you’ll be given warning indications to look out for in case it contracts an infection. At your subsequent session, your damage will be examined.
How do I prevent testicular pain?
While it is not always possible to prevent testicular discomfort, there are specific actions you may take to lessen its underlying causes. These actions comprise:
- Using an athletic supporter to prevent testicular injury
- Engaging in safe sexual behaviour, such as using a condom while having sex
- observing any changes or lumps in your testicles once a month
- To lessen your risk of developing urinary tract infections, empty your bladder after urinating.
If you follow these instructions yet still feel testicular discomfort, consult a doctor immediately.
Conclusion
As shown above, testicles are a critical part of the male fertility process, as they are the sources of sperm generation in men. However, any discomfort, pain or swelling in this area can cause a lot of discomfort and pain in the pubic area. Also, many men go through other sexual and intimate problems, such as Premature Ejaculation and Erectile Dysfunction, which can cause a lot of frustration and confidence issues for them.
However, many online portals such as Ohman’s are giving easy and cost-effective solutions to people, which can help them get out of their intimate issues. All the medicines are FDA approved and do not generally have side effects. For more information about the company and its different products, check out the official site of Ohman. And order your favorite products today.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How long does the discomfort in the testicles take to go away?
Most testicular pain causes are not longer than 6 to 7 weeks. If, in any case, testicular pain takes more time, then you should consult with the doctor.
2. Can I still become Father if I lose a testicle?
Most Men who had their testicles removed but still have one healthy testicle can later become fathers. But in rare cases, when a male is not satisfied with the results chooses to have an artificial or prosthetic testicle.
3. Can testicle pain cause sciatica?
The right and left testicles are similar to one another. Disorders like varicoceles, an expansion of the scrotal vein, may be more likely to affect the left testicle. However, discomfort in either testicle might result from an accident, muscular strain, spinal issues, or sciatica.
4. Is testicular pain normal during puberty?
Teenage testicular discomfort may be an indication of testicular torsion.
The most crucial thing to understand about testicular torsion is that it is a medical emergency that requires prompt attention. Teenage guys, however, may find it challenging to discuss their testicles or to notify their parents if they are in discomfort.



